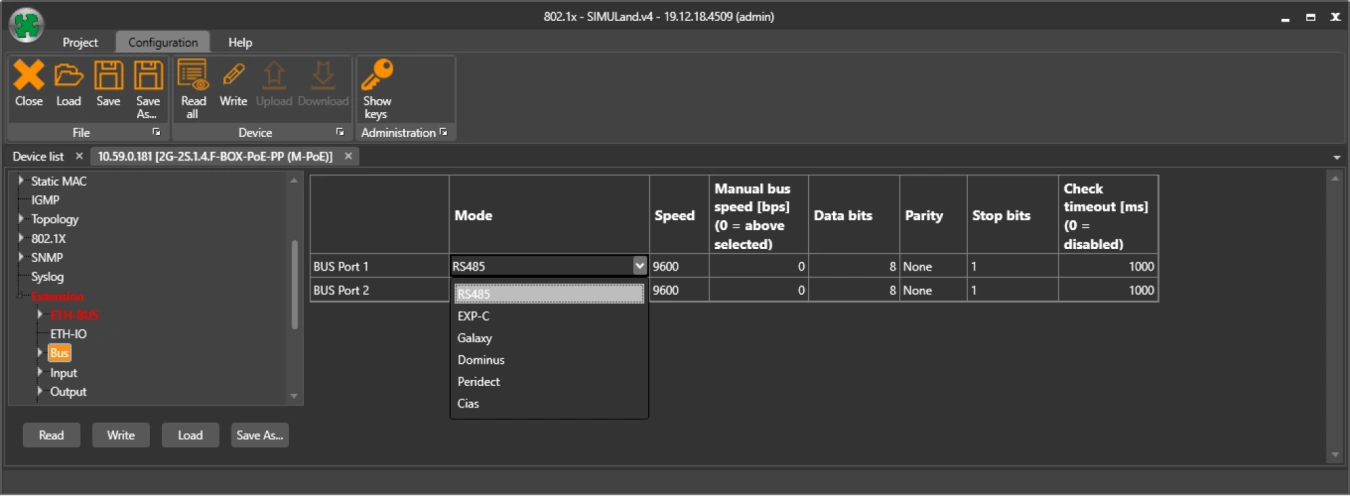
TCP communication over LAN
Update in progress
Connecting sensors via TCP
In a wide range of systems such as e.g:
- Automation systems
- Perimeter protection systems
- Access systems
You need to connect the remote sensors to the software that is installed on the server.
The simplest and most applications supported communication is the so-called TCP connection. For its realization 2 parties are needed:
- TCP client
- TCP server
Establishing and terminating a TCP connection is always initiated by the TCP client. However, beware of a possible mistake !! When collecting data from remote sensors to a server with an application installed, server (hardware) ≠ TCP server. In this case, the TCP server is the IP converter at the sensor and the server (hardware) is the TCP client in terms of the TCP protocol.
Establishing a TCP connection
Because TCP is a connection transport service, a connection must be established between the TCP client and the TCP server before data can be sent. Connection establishment is divided into three steps.
- SYN: The TCP client sends a datagram to the TCP server with the SYN flag set and a randomly generated sequence number (x).
- SYN-ACK: The TCP server sends a datagram to the TCP client with the SYN and ACK flags set and the sequence number (x) incremented by +1. It also generates a random number for its sequence (y).
- ACK: TCP Client sends a datagram with the ACK flag set and with both (x) and (y) sequence numbers incremented by +1.
Both parties (TCP server and TCP client) remember their own sequence number and the counterparty's sequence number. These numbers are used for further communication and determine the order of packets. When the three-way handshaking described above is successful, the connection is established and remains so until the connection is terminated.
Termination of TCP connection
To terminate the data transfer, a connection termination process must take place to release all allocated resources (TCP ports). Datagrams with the FIN and ACK flags are used to terminate the connection. Both sides can initiate the connection termination. Example of TCP client initiated termination:
- The TCP client sends a datagram with the FIN flag set
- The TCP server responds with a datagram with the ACK flag set
- The TCP server sends a datagram with the FIN flag set
- TCP client responds with the ACK flag set
After these steps, the TCP connection is terminated.
Support for TCP connections in METEL devices
METEL IP devices support TCP mode by default on RS485 and RS232 ports. The end devices, which in this case are LAN-RING switches, IPLOG monitoring units or miniLAN serial link converters, are set to TCP server mode. After the TCP port and communication mode have been set up in one step, the connection can be made:
- Automation systems - temperature, humidity, speed, pressure sensors.....
- Perimeter protection systems - perimeter sensors, perimeter sensor evaluation units
- Access control systems - readers
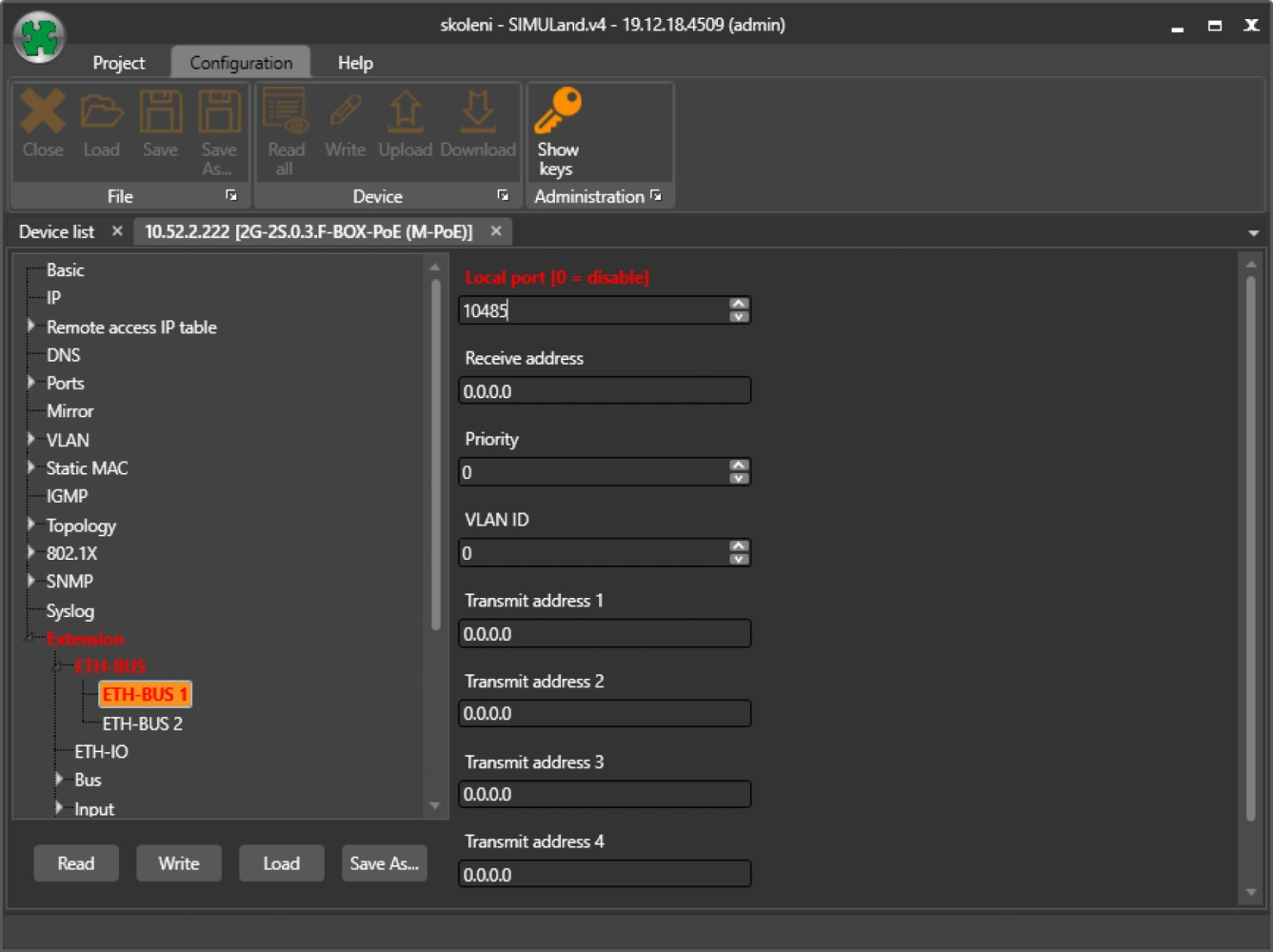
TCP server port settings
Here you set the TCP server port to establish the connection. The TCP protocol uses port numbers (called TCP ports) to distinguish TCP connections. There are a total of 65535 TCP ports, divided into three groups:
- Well-known TCP ports: in the range 0 to 1023 are assigned by IANA and are typically used by system services. Examples: FTP (ports 21 and 20), SMTP (port 25), DNS (port 53) and HTTP (port 80).
- Registered TCP ports: in the range 1024 to 49151. Their use should be registered with ICANN.
- Private TCP ports: in the range 49152 to 65535 are reserved for dynamic allocation and private use. They are not fixed to any application.
For setting the TCP port it is necessary to choose from the so-called private ports.
Setting the serial link mode
Select the correct serial link mode in the BUS menu. In TCP mode, the following options are usually used:
- RS485 - standard RS485 port
- Peridect - optimized for Dominus perimeter systems connected via RS485
- Cias - optimised for CIAS perimeter systems