Redundant topology
Update in progress
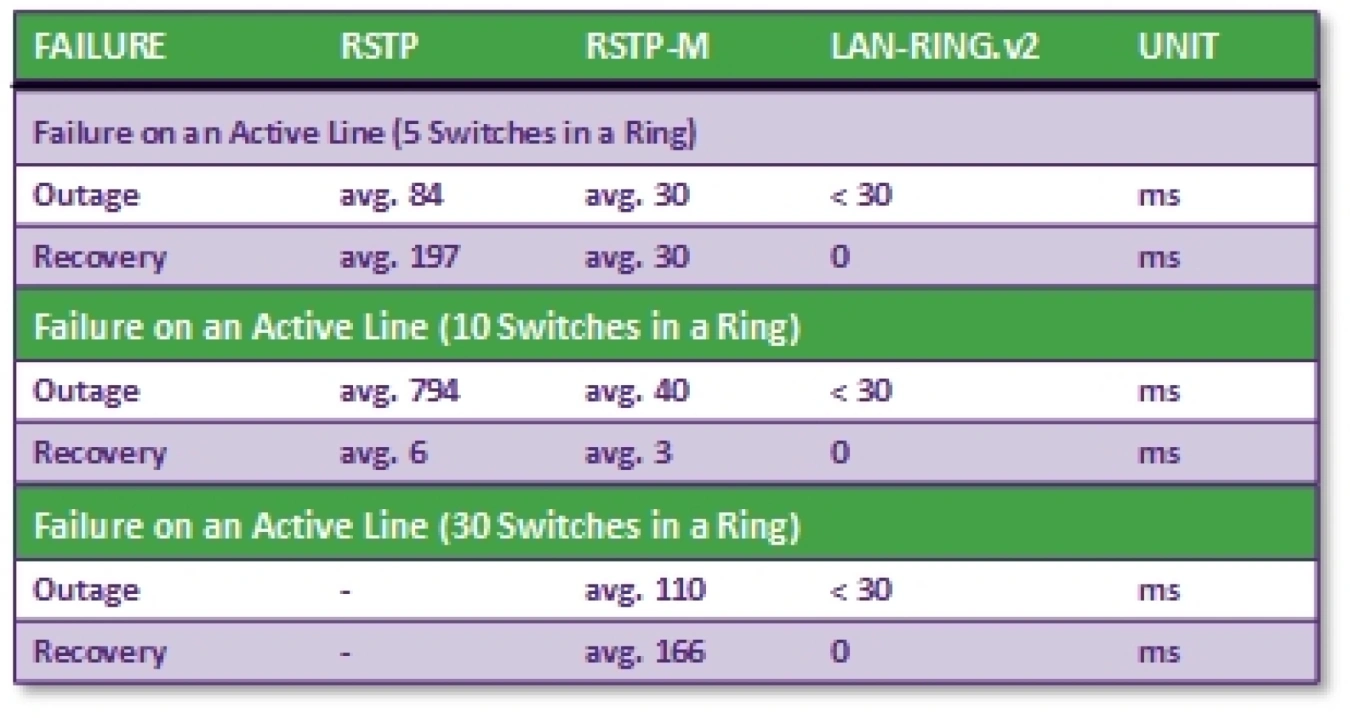
One of the basic security features of the LAN-RING system is the fast redirection of data to a backup line. Since 2008, this function has been performed by the LAN-RING.v1 protocol with a switchover time of up to 30ms from the occurrence of a fault. Each ring in the system has a unique ID and one switch with a MASTER function (controls the ring). The higher port of the MASTER switch is set to BLOCKING mode at rest to prevent loop formation. The port in BLOCKING mode only receives LAN-RING frames and blocks other data (backup link). When an error occurs, the status of the blocked port changes to FORWARDING, and all data are released.
LAN-RING.v1
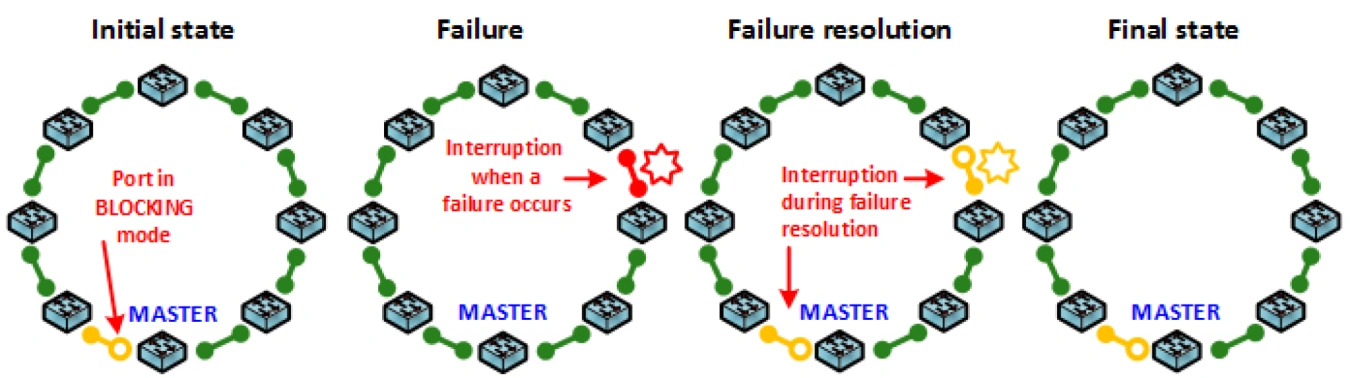
During the fault generation and clearing, the route experiences two short interruptions. The second interruption causes the backup line to return to the MASTER switch. An upgraded version of LAN-RING.v2 has been available since the end of 2014. The MASTER function (the switch with the MASTER function controls the ring) always dynamically moves to the switch adjacent to the fault after the fault occurs. Thus, only one interruption of a maximum of 30ms will occur between the occurrence of the fault and its correction.
LAN-RING.v2
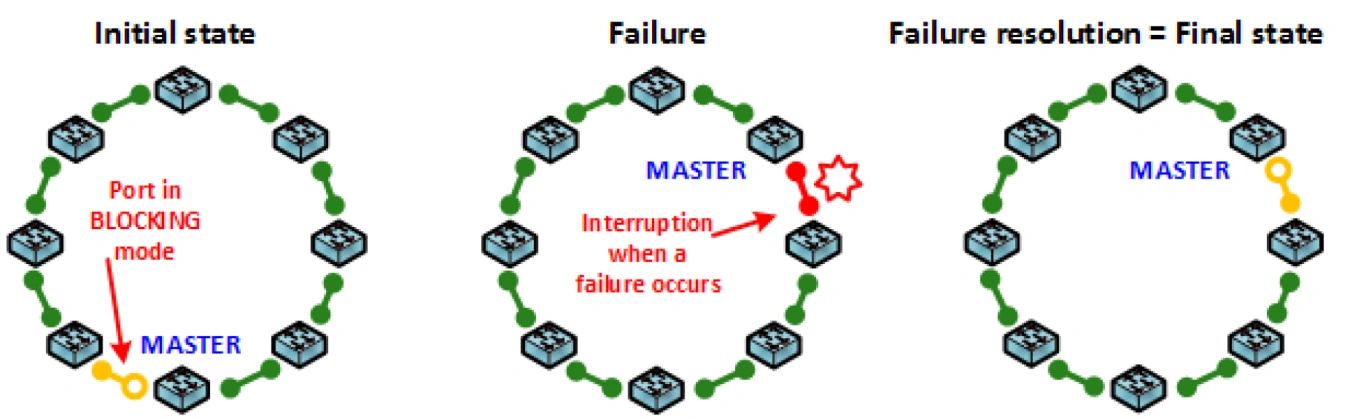
The switchover time to the backup link for LAN-RING protocols negligibly depends on the number of switches connected to the ring. With each switch connected to the ring, the reconfiguration time increases by only about 6μs!
RSTP
The MESH topology is mainly used in larger systems. A prerequisite for its correct functioning is protection against loop formation, often solved by RSTP or MSTP protocols. The advantage of using it on any topology is that it is bought by the non-guaranteed network reconfiguration time in case of failure. Depending on the network's size, the fault's location and the reception of periodically sent BPDU frames (every 2s by default), this ranges from units of ms to units of seconds. The 3rd generation LAN-RING switches support the generic RSTP protocol. The challenging development process has eliminated some imperfections resulting in long network reconfiguration times. The resulting protocol is therefore called RSTP-M. It is backwards compatible with the standardized RSTP protocol.
The table below shows the switching times for the RSTP, RSTP-M and LAN-RING.v2 protocols.